- Blog
SQL is an abbreviation for a Structured Query Language and pronounced either see-kwell or as separate letters. The spread of dynamic websites on the World Wide Web today is largely due to the possibility for their content to be handled through databases. Database management is a complicated process, which has been considerably rationalized by the SQL programming language. As its full name (Structured Query Language) implies, SQL is responsible for querying and editing information stored in a certain database management system.
SQL CREATE TABLE
CREATE TABLE statement is used for creating tables in a database. Tables are organized in rows and columns. Where columns are the attributes and rows are known as records.
CREATE TABLE table_name( column1 datatype, column2 datatype, column3 datatype, ..... column datatype, PRIMARY KEY( one or more columns ) );
CREATE TABLE Example
CREATE TABLE Employees (
EmpID INT NOT NULL,
FirstName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
LastName VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
Age INT NOT NULL,
EmailID VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
PhoneNo INT NOT NULL,
City VARCHAR(25) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (EmpID)
);
The above statement would create a table named “Employees” in the database having the primary key as “EmpID”.
Note: Since EmpID is a primary key it cannot have duplicate values as this column is used for identifying the unique record (row) from the table.
INSERT INTO Statement
The INSERT INTO statement of SQL is used to insert a new row in a table. There are two ways of using the recordset INSERT INTO statement for inserting rows:
Only values: The first method is to specify only the value of data to be inserted without the column names.
Syntax
INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2, value3,…);
Example
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES ('102','Kazim','Mohd','24','kazim@abc.com','1190702985','Delhi'),
('156','Brijesh','Sharma','30','brijesh@abc.com','1187665892','Agra'),
('148','Sakshi','Aswal','25','sakshi@abc.com','1196583701','Bengaluru');
Output

Column names and values both: In the second method we will specify both the columns which we want to fill and their corresponding values.
Syntax
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2, column3,..) VALUES ( value1, value2, value3,..);
Example
INSERT INTO
Employees (
EmpID, FirstName, LastName, Age, EmailID, PhoneNo, City
)
VALUES
('121','Alok','Awasthi','27','alok@abc.com','1149484126','Kanpur'),
('265','Bishwajeet Kumar','Singh','25','bishwajeet@abc.com','1186573520','Noida'), ('164','Nazim','Mohd','22','nazim@abc.com','1109648295','Mumbai'),
(‘312’,’Raman’,’Kumar’,’32’,’raman@abc.com’,’1186047397’,’Kolkata’);
Output

SQL JOINS
A SQL join is an SQL clause that is used to join records from two or more tables in a database. The records from the tables are combined by a common attribute that the tables share, resulting in a single record set. This record set can be inserted into a temporary table to be stored and used. You can also specify additional criteria in the join to filter out records (besides sharing the common attribute).
Types of JOINS
- SQL INNER JOIN (JOIN)
- SQL LEFT OUTER JOIN (LEFT JOIN)
- SQL RIGHT OUTER JOIN (RIGHT JOIN)
- SQL FULL OUTER JOIN (FULL JOIN)
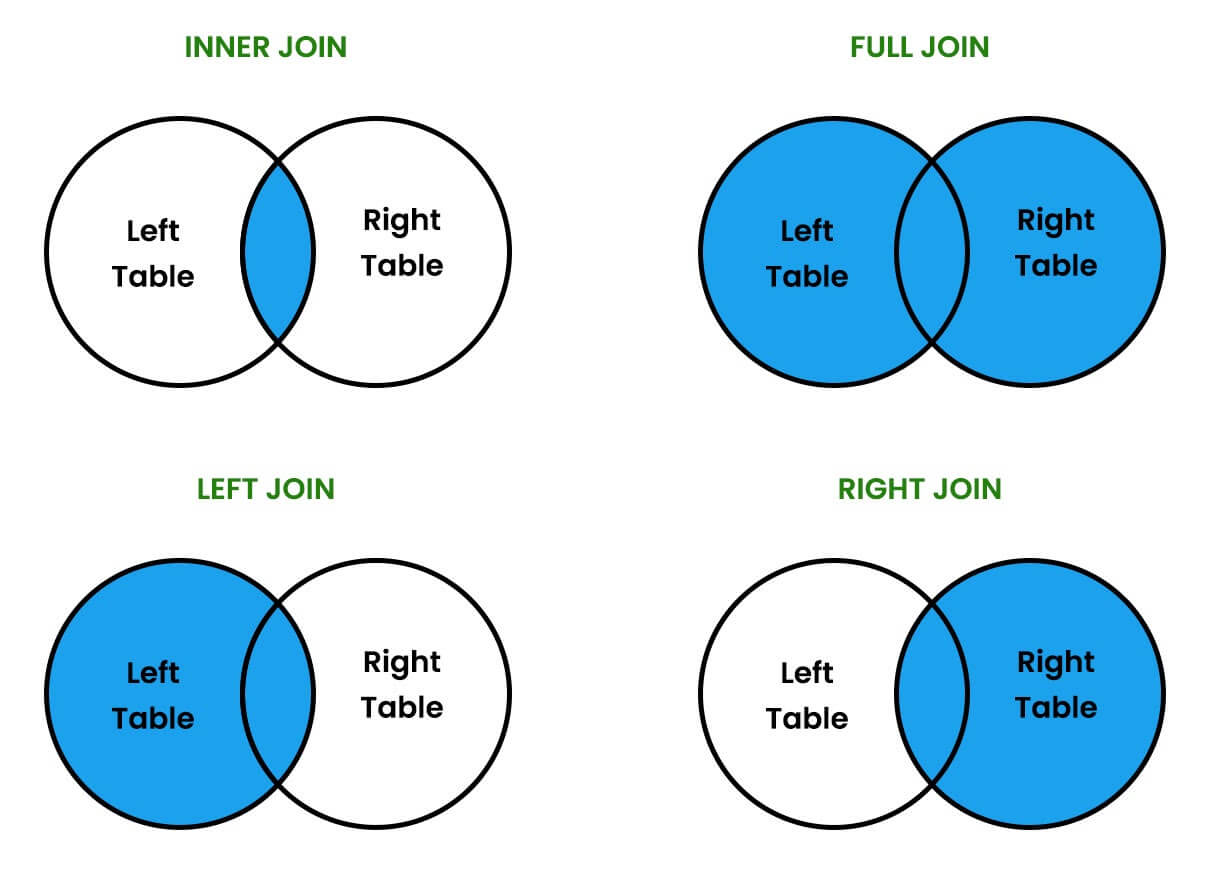
Let us look into each one of them. For your better understanding of this concept, I will be considering the following three tables to show you how to perform the Join operations on such tables.
Employees Table

Projects Table

Clients Table

INNER JOIN
Inner join is the most commonly used. It only combines records from the two tables if they both match the join condition (share a common attribute). This joins work best when referential integrity is enforced in the database, especially on primary and foreign keys.
Syntax
SELECT Table1.Column1,Table1.Column2,Table2.Column1,Table2.Column2,.... FROM Table1 INNER JOIN Table2 ON Table1.MatchingColumnName = Table2.M
Example
SELECT Employees.EmpID, Employees.FirstName,Projects.ProjectID,Projects.ProjectName,Projects.ProjectStartDate FROM Employees INNER JOIN Projects ON Employees.EmpID=Projects.EmpID;
Output

LEFT JOIN
The left join means that the join will favor the left listed (first listed) table. Favoring the table means that all results from that table will be shown in the result, whether or not they match the joined table on the condition. If they do not match any rows in the joined table, they will be attached to null columns.
Syntax
SELECT Table1.Column1,Table1.Column2,Table2.Column1,Table2.Column2.... FROM Table1 LEFT JOIN Table2 ON Table1.MatchingColumnName = Table2.MatchingColumnName;
Example
SELECT Employees.EmpID, Employees.FirstName, Projects.ProjectID, Projects.ProjectName FROM Employees LEFT JOIN Projects ON Employees.EmpID = Projects.EmpID ;
Output

RIGHT JOIN
A right join returns all rows from the RIGHT-hand table specified in the ON condition and only those rows from the other table where the joined fields are equal (join condition is met).
SELECT Table1.Column1,Table1.Column2,Table2.Column1,Table2.Column2.... FROM Table1 RIGHT JOIN Table2 ON Table1.MatchingColumnName = Table2.MatchingColumnName;
Example
SELECT Projects.ProjectID,Projects.ProjectName,Clients.ClientID,Clients.ClientName FROM Projects RIGHT JOIN Clients ON Projects.ClientID = Clients.ClientID;
Output

FULL JOIN
A full join means that both tables are favored, so all rows from each table will be listed in the result regardless of whether they match any rows in the other table. In practice, these joins are fairly rare.
Syntax
SELECT Table1.Column1,Table1.Column2,Table2.Column1,Table2.Column2,.... FROM Table1 FULL JOIN Table2 ON Table1.MatchingColumnName = Table2.MatchingColumnName;
Example
SELECT Projects.ProjectID,Projects.ProjectName,Clients.ClientID,Clients.ClientName FROM Projects FULL JOIN Clients ON Projects.ClientID = Clients.ClientID;
Output

Conclusion
SQL joins are commonplace in the database world as normalized databases contain many tables. Without them, there would not be an efficient way to retrieve the data that you are looking for. Utilizing the four types will help you write better queries, and retrieve the proper data efficiently.