Incubation period
n., [ˌɪn kyəˈbeɪ ʃən ˈpɪɹ.i.əd]
Definition: The period between the initial infection and the onset of signs and symptoms
Table of Contents
Incubation Period Definition
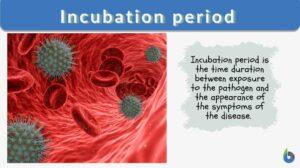
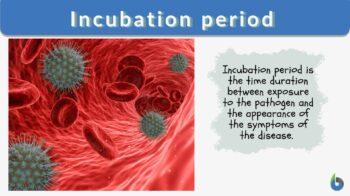
The incubation period is the time duration between exposure to the pathogen and the appearance of the disease symptoms. In epidemiology, the incubation period implies the duration taken by the pathogen to multiply to reach the threshold beyond which clinical symptoms start appearing. The incubation period differs for each pathogen; for example, the Influenza virus of the flu, the incubation period is one day whereas the incubation period of the measles virus is around 12 days. Hepatitis virus takes approximately four weeks to exhibit any clinical symptoms. In comparison, the chickenpox incubation period is about 2 to 3 weeks to show clinical symptoms after exposure. Canine Parvovirus of dogs has an incubation period of 3 – 7 days.
In the current context, it is pertinent to know: How long is the incubation period of coronavirus?
The viral incubation period for coronavirus varies between 1-14 days; however, the incubation time is around five days in most patients. Hence, the incubation period COVID is considered to be five days.
The incubation period or incubation phase of a pathogen is an essential parameter in disease epidemiology as it reflects the efficiency of the control measures in controlling the infection. It also helps to map out the strategies to control the spread of infection.
Any pathogenic disease development undergoes four stages of infection. They are as follows:
- Stage 1- Incubation period of infection
- Stage 2- Prodromal period of infection
- Stage 3- Acute period of infection
- Stage 4- Convalescence period of infection
As per the time, different stages of infection can be defined, and these stages are characteristic of an epidemiologic infectious disease. The infection in the body is initiated by the entry of the pathogen, which is defined as ‘exposure‘. After the exposure, the pathogen will get transferred to the organ or tissue in the body where the conditions for its survival are optimum, and it can multiply to establish the infection. For example, the liver is the site for the multiplication of the hepatitis virus and the COVID-19 virus multiplies in the lungs. Once the pathogen starts multiplying, the body’s immune system gets activated. Although, at this stage, the clinical symptoms of the disease may not be present. However, the infection may be diagnosed with the help of laboratory diagnostic tests. The disease may be classified as ‘symptomatic‘ and ‘asymptomatic’ at this stage. The time between exposure and infection is known as the ‘latent period.’ In the latency period, the clinical symptoms are not manifested.
So, what is “incubation period”? In this context, the meaning of incubation period is the duration between exposure to the pathogen and the onset of symptoms. This particular period characterizes or defines the ‘incubation period’ (also referred to as the ‘incubation stage of infection’). Hence, in this stage, the manifestation of clinical symptoms occurs, i.e., at the incubation period disease is symptomatic. Each pathogenic organism undergoes the stages of incubation in the host.
The host may transmit infection at any stage of infection; however, it may differ from pathogen to pathogen. So now the question arises, how long are viral infections contagious? Usually, a period of 2 weeks is considered to be contagious. Nevertheless, it varies from pathogen to pathogen.
Different stages of infection have been depicted figuratively in Figure 1 for better understanding.
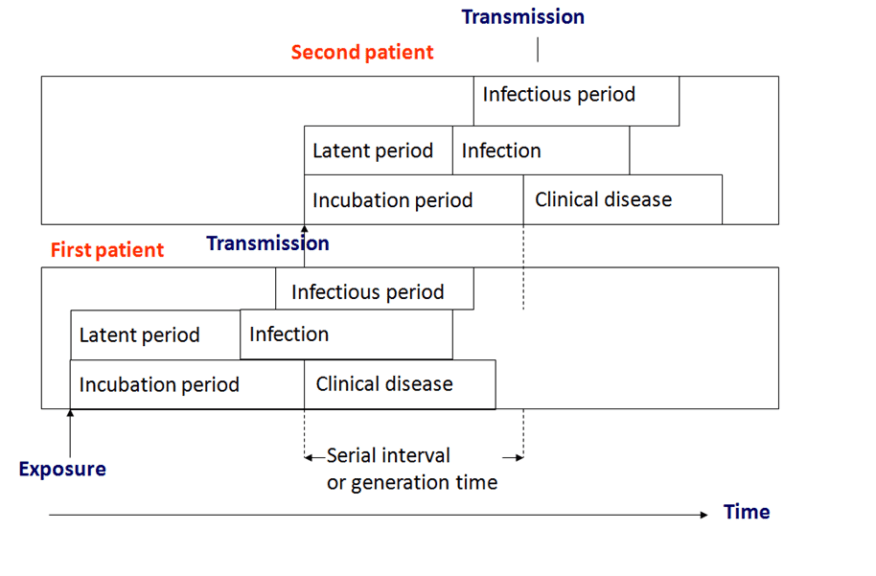
The incubation period is the period between the initial infection and the onset of signs and symptoms. The incubation period is the initial stage of an infectious disease. During this stage, the pathogens are actively dividing and growing in number. The duration of the incubation period may vary depending on various factors, such as the immunocompetence of the host and the virulence of the pathogen. The next stage after the incubation period is the prodromal stage.See also:
Intrinsic and Extrinsic Incubation Period
The terms intrinsic and extrinsic incubation periods are applicable for vector-borne diseases.
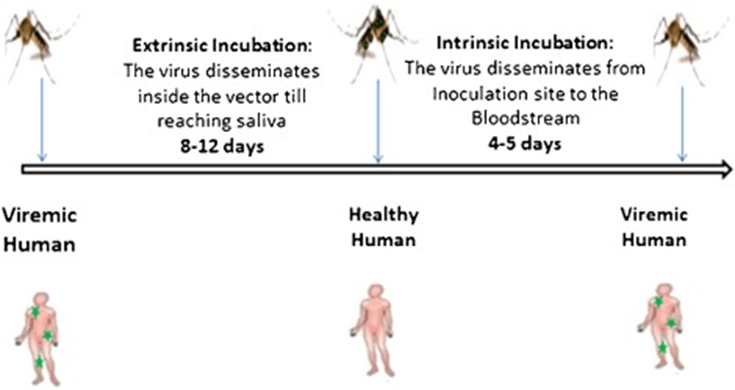
- The intrinsic incubation period is the duration between pathogen exposure and the appearance of symptoms of the disease in the definitive host.
- The extrinsic incubation period is the duration required for the complete development of the pathogen in the intermediate host. For example, it takes 28 days for the malaria parasite’s gametocyte stage to develop into the sporozoite stage in the mosquito body. Hence, 28 days is the extrinsic incubation period of the malarial parasite. The extrinsic incubation period of the malaria parasite is also known as sporogony, which is the duration between ingestion of gametocyte stage via infected blood meal to the stage where sporozoite stage reaches the salivary gland of the mosquito, making it capable of transmitting the infection. The extrinsic incubation period in malaria is affected by various factors like temperature, genetic diversity of the parasite and vector, biotic and abiotic factors. Thus, the incubation period of malaria ranges from 7 to 30 days.
The intrinsic and extrinsic incubation periods can be understood with the help of a diagrammatic illustration of the infection cycle of the Zika virus (Figure 2).
Determining Factors
The incubation period of a pathogen is dependent upon a number of factors, that includes-
- Duration of exposure to the pathogen
- Amount or dose of the pathogen on exposure
- Route of entry of the pathogen
- Vulnerability or predisposition of the host to the pathogen
- Rate of the multiplication of pathogen in the host
- Host defense system
Examples for Diseases in Humans
The answer to the question ‘what is the average incubation period for a virus’ is pretty dramatic as the virus incubation period may vary from 1 day to year(s). Some of the examples of the viral incubation period of pathogens are as mentioned below:
- Incubation period covid- 19 virus: 5 to 6 days
- Delta variant incubation period: 2-3 days
- Chickenpox incubation period: 2 to 3 weeks
- Shingles incubation period: 7 to 10 days
- Flu incubation period: 2 days
- Common cold incubation period: 1 to 3 days
- HIV incubation period: around four weeks or one month
- Rabies incubation period: few days to a year
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus or RSV incubation period: 2 to 8 days
- Salmonella incubation period: 12 to 72 hours
- Cough or croup incubation period: 2- 5 days
- Stomach flu incubation period or stomach bug incubation period: 24 to 48 hours
- Group A Strep pharyngitis or Strep incubation time: The incubation period of Strep throat ranges from 2 to 5 days
- E. coli incubation period: 3 to 4 days
- Mumps incubation period: 16- 18 days
- Pink eye incubation period: 24 to 72 hours
- Tetanus incubation period: 3 to 21 days
- Roseola incubation period: 5 to 15 days
- Ebola incubation period: 2 to 21 days
- Pneumonia incubation period: 2 to 5 days
- Listeria incubation period: 1 to 2 weeks
- Rotavirus incubation period: 2 days
- Scabies incubation period:4 to 8 weeks
- Ringworm incubation period: 10 to 14 days
- Tonsillitis incubation period: 2 to 4 days
- Rubella incubation period: 12 to 23 days
- The incubation period of hepatitis b: 90 days
- The incubation period of tuberculosis: few months to two years
- The incubation period of cholera: 2 hours to 5 days
- The incubation period of diphtheria: 2 to 5 days
Sexually transmitted diseases or STD incubation period:
- Chlamydia incubation period: 7 to 21 days
- Herpes incubation period or Genital herpes incubation period: 4 days
- Gonorrhea incubation period: 2 to 5 days
- Syphilis incubation period: 21 days
- Hepatitis A incubation period: 15 to 50 days
Try to answer the quiz below to check what you have learned so far about the incubation period.
References
- Lai, C., Yu, R., Wang, M., Xian, W., Zhao, X., Tang, Q., Chen, R., Zhou, X., Li, X., Li, Z., Li, Z., Deng, G., & Wang, F. (2020). Shorter incubation period is associated with severe disease progression in patients with COVID-19. Virulence, 11(1), 1443–1452. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2020.1836894
- Ohm, J.R., Baldini, F., Barreaux, P. et al. Rethinking the extrinsic incubation period of malaria parasites. Parasites Vectors 11, 178 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-018-2761-4
- Rothman K. J. (1981). Induction and latent periods. American journal of epidemiology, 114(2), 253–259. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113189
- Virlogeux, V., Fang, V. J., Wu, J. T., Ho, L. M., Peiris, J. S., Leung, G. M., & Cowling, B. J. (2015). Brief Report: Incubation Period Duration and Severity of Clinical Disease Following Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection. Epidemiology (Cambridge, Mass.), 26(5), 666–669. https://doi.org/10.1097/EDE.0000000000000339
©BiologyOnline.com. Content provided and moderated by Biology Online Editors.