- 1. K.LOHITHA
PA/2016/106
National Institute of Pharmaceutical
Education and Research (NIPER)
Pharmacopoeial methods of Analysis
- 2. Sterility – Process of removing all viable forms of microorganisms.
Sterility test – A test that critically assesses whether a sterilized pharmaceutical
product is free from contaminating microorganisms.
(or)
Acc to IP – The sterility tests are intended for testing the absence of viable forms of
microorganisms in or on the pharmacopeial preparations.
- 3. Products which are necessary to be sterilized :
• Injections
• Implants
• Syringes
• Ophthalmic preparations
• Ointments & creams
• Bandages
• Surgical dressings & devices
• needles
- 4. • These tests are based upon the principle that if micro-
organisms (present in the sample) are placed in a medium
which provides nutritive material and water, and kept at a
favorable temperature, the organisms will grow and their
presence can be indicated by a turbidity in the originally clear
medium.
• The interpretation of results is based on the assumption that
the contents of every container in the batch, had they been
tested, would also have given the same results.
• Since every container cannot be tested, a sufficient number of
containers should be examined to give a suitable degree of
confidence in the results of the tests.
PRINCIPLE
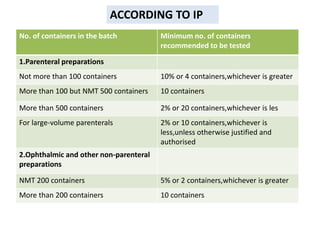
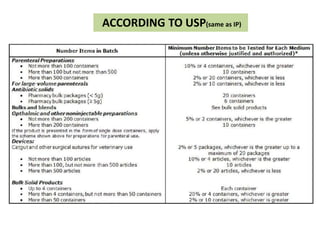
- 5. No. of containers in the batch Minimum no. of containers
recommended to be tested
1.Parenteral preparations
Not more than 100 containers 10% or 4 containers,whichever is greater
More than 100 but NMT 500 containers 10 containers
More than 500 containers 2% or 20 containers,whichever is les
For large-volume parenterals 2% or 10 containers,whichever is
less,unless otherwise justified and
authorised
2.Ophthalmic and other non-parenteral
preparations
NMT 200 containers 5% or 2 containers,whichever is greater
More than 200 containers 10 containers
ACCORDING TO IP
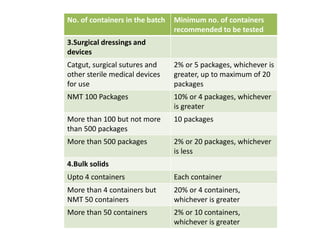
- 6. No. of containers in the batch Minimum no. of containers
recommended to be tested
3.Surgical dressings and
devices
Catgut, surgical sutures and
other sterile medical devices
for use
2% or 5 packages, whichever is
greater, up to maximum of 20
packages
NMT 100 Packages 10% or 4 packages, whichever
is greater
More than 100 but not more
than 500 packages
10 packages
More than 500 packages 2% or 20 packages, whichever
is less
4.Bulk solids
Upto 4 containers Each container
More than 4 containers but
NMT 50 containers
20% or 4 containers,
whichever is greater
More than 50 containers 2% or 10 containers,
whichever is greater
- 7. ACCORDING TO IP
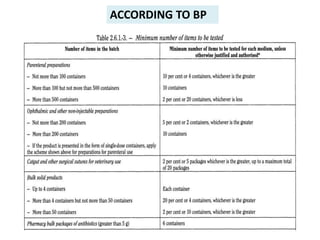
- 8. ACCORDING TO BP
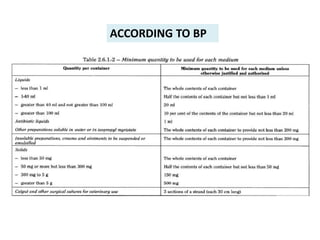
- 9. ACCORDING TO BP
- 10. ACCORDING TO USP(same as IP)
- 11. ACCORDING TO USP(same as IP)
except
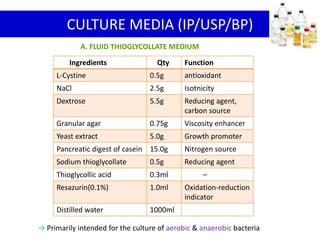
- 12. Ingredients Qty Function
L-Cystine 0.5g antioxidant
NaCl 2.5g Isotnicity
Dextrose 5.5g Reducing agent,
carbon source
Granular agar 0.75g Viscosity enhancer
Yeast extract 5.0g Growth promoter
Pancreatic digest of casein 15.0g Nitrogen source
Sodium thioglycollate 0.5g Reducing agent
Thioglycollic acid 0.3ml –
Resazurin(0.1%) 1.0ml Oxidation-reduction
indicator
Distilled water 1000ml
A. FLUID THIOGLYCOLLATE MEDIUM
CULTURE MEDIA (IP/USP/BP)
→ Primarily intended for the culture of aerobic & anaerobic bacteria
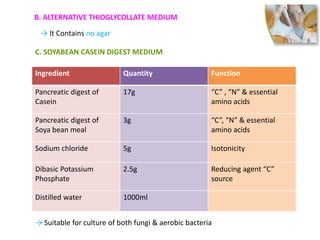
- 13. Ingredient Quantity Function
Pancreatic digest of
Casein
17g “C” , “N” & essential
amino acids
Pancreatic digest of
Soya bean meal
3g “C”, “N” & essential
amino acids
Sodium chloride 5g Isotonicity
Dibasic Potassium
Phosphate
2.5g Reducing agent “C”
source
Distilled water 1000ml
→ It Contains no agar
B. ALTERNATIVE THIOGLYCOLLATE MEDIUM
C. SOYABEAN CASEIN DIGEST MEDIUM
→ Suitable for culture of both fungi & aerobic bacteria
- 14. MEDIA SUITABILITY TEST
Media is sterile
Prior to test, make sure that :
Media supports growth of microorganisms
2 components in Media suitability test :
Media sterility test
Growth Promotion test
- 15. MEDIA SUITABILITY TEST - ctnd
- 16. MEDIA SUITABILITY TEST - ctnd
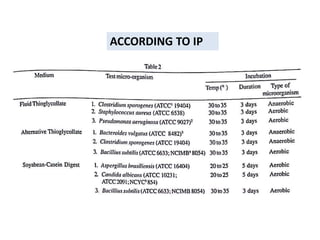
- 17. ACCORDING TO IP
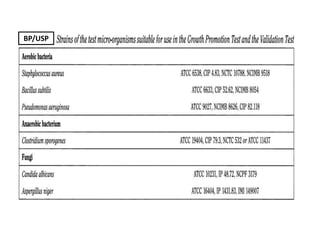
- 18. BP/USP
- 19. VALIDATION TEST(IP/BP/USP)
Carry out a test as described below under Test for Sterility of
the Product to be Examined using exactly the same methods,
except for the following modifications.
Membrane Filtration
After transferring the content of the container or containers
to be tested to the membrane, add an inoculum of a small
number of viable microorganisms (not more than 100 cfu) to
the final portion of sterile diluent used to rinse the filter.
Direct Inoculation
After transferring the contents of the container or
containers to be tested to the culture medium, add an
inoculum of a small number of viable microorganisms (not
more than 100 CFU) to the medium
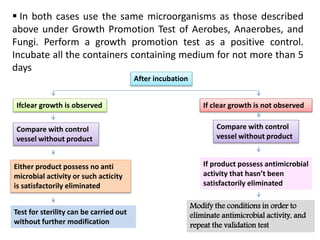
- 20. In both cases use the same microorganisms as those described
above under Growth Promotion Test of Aerobes, Anaerobes, and
Fungi. Perform a growth promotion test as a positive control.
Incubate all the containers containing medium for not more than 5
days
After incubation
Ifclear growth is observed If clear growth is not observed
Compare with control
vessel without product
Either product possess no anti
microbial activity or such acticity
is satisfactorily eliminated
If product possess antimicrobial
activity that hasn’t been
satisfactorily eliminated
Test for sterility can be carried out
without further modification
Modify the conditions in order to
eliminate antimicrobial activity, and
repeat the validation test
Compare with control
vessel without product
- 21. This validation is performed
(a)when the test for sterility has to be carried out on a new
product; and
(b whenever there is a change in the experimental conditions of
the test. The validation may be performed simultaneously
with the Test for Sterility of the Product to be Examined
VALIDATION TEST - ctnd
- 22. It is preferred where the substance under examination is :
• An oil
• An ointment that can be put into the solution
• A non bacteriostatic solid not readily soluble in the
culture medium.
• A soluble powder or a liquid that possess inherent
bacteriostatic or fungistatic properties.
• For liquid products where the volume in a container
is 100m1 or more.
A. MEMBRANE FILTRATION
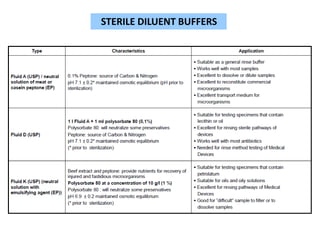
- 23. STERILE DILUENT BUFFERS
- 24. • A membrane has a nominal pore size not greater than 0.45μ and
diameter of approximately 50mm.
• This method basically involves filtration of Sample through
membrane filters.
PROCEDURE :
- 25. • The filtration is assisted under strict aseptic condition. After
filtration gets completed, remove the membrane from the
holder aseptically.
• Cut into 2 halves. Place each half in a suitable volume (usually
100ml) of FTM and SCDM respectively and incubate.
Incubation
Period : at least 14 days incubation
Temperature : 30-35° C for FTM
20-25 ° C for SCD
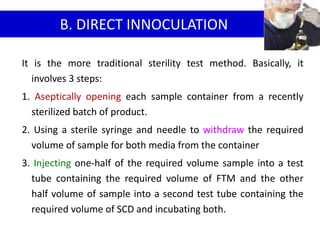
- 26. It is the more traditional sterility test method. Basically, it
involves 3 steps:
1. Aseptically opening each sample container from a recently
sterilized batch of product.
2. Using a sterile syringe and needle to withdraw the required
volume of sample for both media from the container
3. Injecting one-half of the required volume sample into a test
tube containing the required volume of FTM and the other
half volume of sample into a second test tube containing the
required volume of SCD and incubating both.
B. DIRECT INNOCULATION
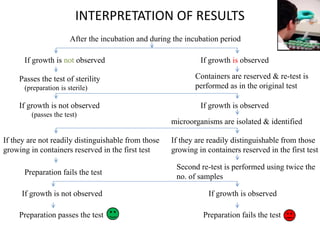
- 27. After the incubation and during the incubation period
If growth is not observed If growth is observed
Passes the test of sterility
(preparation is sterile)
Containers are reserved & re-test is
performed as in the original test
If growth is not observed
(passes the test)
If they are not readily distinguishable from those
growing in containers reserved in the first test
Preparation fails the test
If growth is not observed
Preparation passes the test
INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS
microorganisms are isolated & identified
If growth is observed
If they are readily distinguishable from those
growing in containers reserved in the first test
Second re-test is performed using twice the
no. of samples
If growth is observed
Preparation fails the test
- 28. REFERENCES
INDIAN PHARMACOPOEIA2014,
VOLUME 1(59-66)
UNITED STATES PHARMACOPOEIA
2013, VOLUME 1(71-76)
BRITISH PHARMACOPOEIA2009,
VOLUME 4(Appendix XVI)