- 1. CS 603
Distributed Transactions
February 18, 2002
- 2. What is a Transaction?
• Atomic
– The external view is that either everything in the
transaction happened, or nothing did
• Consistent
– If the start state is valid, the end state is valid
• Isolated
– A transaction in process is not affected by and does
not affect any other transaction
• Durable
– Once complete, the effects of a transaction are
permanent, even in the event of failure.
- 3. Distributed Transactions
• What is the difference with Distributed
Transactions?
– NOTHING!
– Must still support ACID properties
– Important for all the same reasons
• Why do we study Distributed
Transactions?
– Some properties harder to implement
– Basic single-system techniques not sufficient
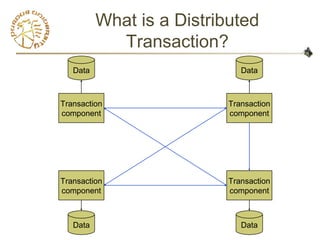
- 4. What is a Distributed
Transaction?
Data
Transaction
component
Transaction
component
Data
Data
Transaction
component
Transaction
component
Data
- 5. Why are Distributed
Transactions Hard?
• Atomic
– Different parts of a transaction may be at different
sites
– How do we ensure all or none committed?
• Consistent
– Failure may affect only part of transaction
• Isolated
– Commitment must occur “simultaneously” at all sites
• Durable
– Not much different when other problems solved
– Makes “delayed commit” difficult
- 6. Key Issues
• Commitment
– Standard techniques preserve properties
when commit occurs
– Distributed systems need commit protocols so
we know when commit has occurred
• Failures
– Standard techniques support durability for
commit/abort
– What happens if a site fails during
commitment?
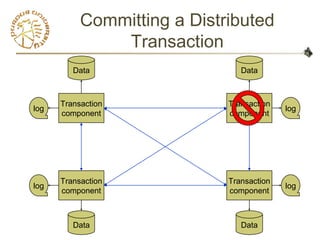
- 7. Committing a Distributed
Transaction
Data
Transaction
component
log
Transaction
component
Data
log
Data
Transaction
component
log
Transaction
component
Data
log
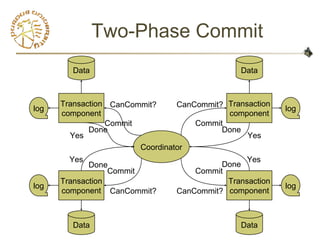
- 8. Two-Phase Commit
(Lamport ’76, Gray ’79)
• Assumes central coordinator
– Coordinator initiates protocol
– Participants: entities with actions to be
committed/aborted
• Phase 1:
– Coordinator asks if participants can commit
– Participants respond yes/no
• Phase 2:
– If all votes yes, coordinator sends Commit
• Otherwise send Abort
– Participants send Have Committed / Have Aborted
- 9. Two-Phase Commit
Data
Transaction
component
log
Done Done
Done
Transaction
component
Data
log
Data
Transaction
component
log
Done
Transaction
component
Data
log
CanCommit? CanCommit?
Coordinator
Commit
CanCommit? CanCommit?
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Commit
Commit Commit
- 10. Two-Phase Commit:
Fault Tolerance
• Participant fails in Phase 1:
– Coordinator doesn’t get unanimous yes
– Abort
• Participant fails in Phase 2:
– On reawakening, can ask coordinator if it
should commit or abort
– Requires that both commit and abort states
be durable before sending “yes” vote
- 11. Two-Phase Commit:
Problems
• Blocks on failure
– Timeout before abort if participant fails
– All participants must wait for recovery if
coordinator fails
• While blocked, transaction must remain
Isolated
– Hold locks on data items touched
– Prevents other transactions from completing
• Solution: Wednesday