- 1. The Circulatory System SBI3U
- 2. Interesting Facts Your system of blood vessels – arteries, veins and capillaries – is over 60,000 miles long. That's long enough to go around the world more than twice! The adult heart pumps about 5 quarts of blood each minute – approximately 2,000 gallons of blood each day – throughout the body.
- 3. Interesting Facts When attempting to locate their heart, most people place their hand on their left chest. Actually, your heart is located in the center of your chest between your lungs. The bottom of the heart is tipped to the left, so you feel more of your heart on your left side of your chest. The heart beats about 100,000 times each day.
- 4. Interesting Facts In a 70-year lifetime, the average human heart beats more than 2.5 billion times An adult woman’s heart weighs about 8 ounces, a man’s about 10 ounces A child’s heart is about the size of a clenched fist; an adult’s heart is about the size of two fists. Blood is about 78 percent water. Blood takes about 20 seconds to circulate throughout the entire vascular system.
- 5. Overview of Circulation Cardiac circulation: blood flow within the heart Pulmonary circulation: blood flow between the heart and lungs Systemic circulation: blood flow from heart to rest of the body
- 6. The pathway of blood flow Heart Vein Artery Venule Arteriole Capillary
- 7. Types of Blood vessels Vessel Structure Function Diagram Artery Thick elastic walls Small circumference Transports blood AWAY from the heart Vein Thin, less elastic walls with valves Large circumference Transports blood TOWARDS the heart Capillary Very thin wall Smallest circumference Materials are exchanged between the blood and the body
- 8. Arteries and veins A. Cross-section B. Longitudinal section
- 9. Capillaries Walls of blood vessels are made up of cells called endothelial cells . The thin layer of endothelial cells allows diffusion to occur more rapidly.
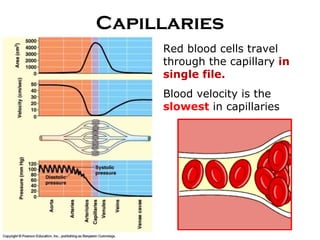
- 10. Capillaries Red blood cells travel through the capillary in single file. Blood velocity is the slowest in capillaries
- 11. Why blood flows In arteries: Elastic walls expand and contract. As they contract, this helps to pump the blood around the body. 3 structural layers. Outer layer - covering of connective tissue. Middle layer (thickest layer) - alternating circular bands of elastic fibres and smooth muscle Inner layer - only a single cell thick, contains smooth endothelial cells that serve to reduce friction as blood courses through the artery.
- 12. Why blood flows In veins: Valves act as one-way doors to prevent blood from flowing backwards . Muscular contractions can “pump” the blood
- 13. Varicose veins When valves don’t work properly
- 14. What is in blood? -red blood cells (erythrocyte) carry oxygen -white blood cells (leucocytes) part of the immune system -platelets stop bleeding by clotting blood -plasma contains nutrients like amino acids and glucose -water
- 15. The human heart
- 16. Direction of blood flow Oxygenated blood: Lung pulmonary vein left atrium bicuspid valve left ventricle aortic semilunar valve aorta rest of body Deoxygenated blood: Vena cava tricuspid valve right atrium right ventricle pulmonary semilunar valve pulmonary artery lungs
- 17. Cardiac Circulation
- 18. Cardiac Circulation
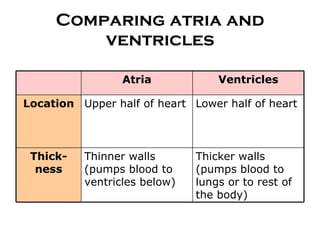
- 19. Comparing atria and ventricles Atria Ventricles Location Upper half of heart Lower half of heart Thick-ness Thinner walls (pumps blood to ventricles below) Thicker walls (pumps blood to lungs or to rest of the body)
- 20. The heartbeat The heartbeat is controlled by the sinoatrial node (also known as the pacemaker ). The SA node sends electrical signals that cause the heart muscle to contract. The heart makes a ‘lup-dup ’ sound as blood flows through and the valves close.
- 21. The SA node and the AV node SA node = sinoatrial node AV node = atrioventricular node
- 22. Electrocardiographs (ECGs) The electrical signals of the heart can be measured using a machine called an electrocardiograph ( ECG ).
- 23. ECG analysis P: atria contract (ventricles relax) QRS: ventricles contract (atria relax) T: both atria and ventricles relax
- 24. Cardiovascular disease AORTIC ANEURYSM
- 25. Cardiovascular disease ATHEROSCLEROSIS
- 26. Treatments CORONARY BYPASS
- 27. Treatments ANGIOPLASTY & STENT
- 28. Mammalian Heart
- 29. Pericardium
- 30. Tricuspid Valve
- 31. Bicuspid Valve
- 32. Chordae Tendinae “the heart strings”
- 33. Prosthetic Valves