- Home
- >
- Attribute | Definition & Meaning
JUMP TO TOPIC
- Definition
- Database Management System
- Entity-relationship Diagram
- Types of Attributes in ER Diagram
- Simple Attributes
- Composite Attributes
- Single Valued Attributes
- Multi-valued Attributes
- Derived Attributes
- Key Attributes
- Entity Set
- Strong Entity Set
- Weak Entity Set
- Types of Attributes in Data Mining
- Qualitative Attributes
- Quantitative Attributes
- Example
- Solution
Attribute|Definition & Meaning
Definition
An attribute is defined as a property of a living thing or an object. For example, a tiger’s attributes include speed, height, and color. In Database Management System, attributes are used to provide organization and structure to a database. An attribute, also known as metadata, consists of a value and a name of an object.
Figure 1 shows a ball whose attributes include its shape, i.e., round or a sphere, and its color, i.e., blue.
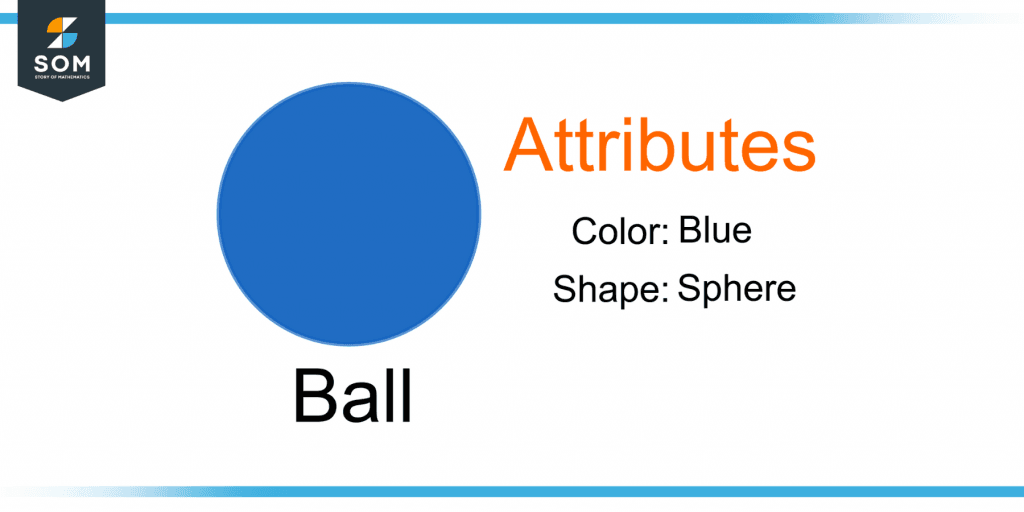
Figure 1 – Demonstration of Attributes of a Ball
Database Management System
Database Management System(DBMS) deals with storing, retrieving, compiling, and organizing data in the system software. It acts as an interface between the database and the end user. The users are allowed to delete, update, read, and create data in the system.
Attributes play an essential role in DBMS. They are used to define the properties of a specific object.
Entity-relationship Diagram
An Entity-Relationship Diagram, abbreviated as ERD, is used to show the relationship between different entities such as people, places, objects, or events in a database System.
An ERD is a graphical representation of the database structure. An elliptical shape is used to represent an attribute of an entity in an ERD.
Different styles of elliptical shapes are used to differentiate between different types of attributes. Figure 2 shows the different styles for each type of attribute in an ER diagram.
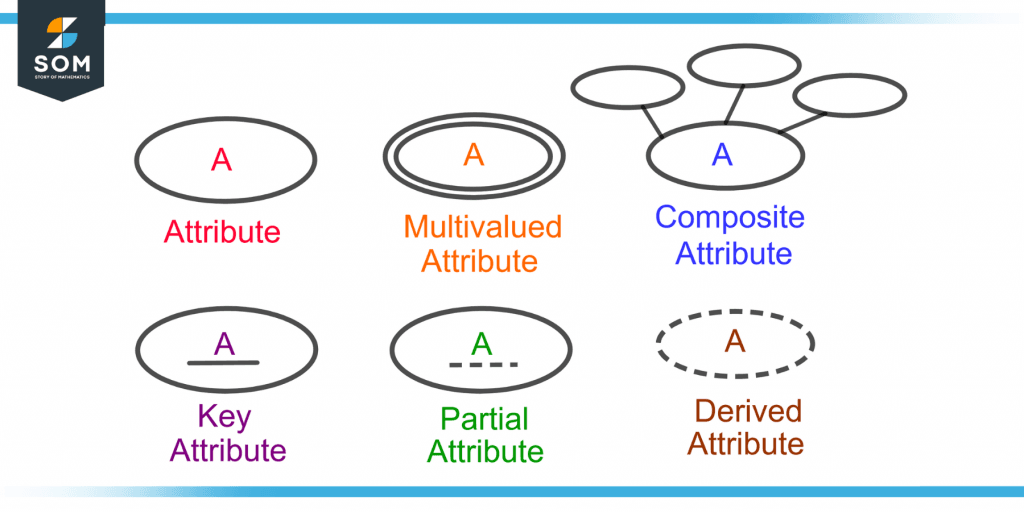
Figure 2 – Graphical Representation of Different Types of Attributes in an Entity Relationship Diagram
Types of Attributes in ER Diagram
The different types of attributes used in Entity-Relation Diagrams are discussed below.
Simple Attributes
As the name suggests, simple attributes cannot be subdivided further. For example, a student’s age, class, and roll number are all simple attributes.
Composite Attributes
Composite attributes are composed of many simple attributes. It means that they can be further divided into simple attributes.
For example, a name of a person is a composite attribute as it is composed of his first name, middle name, and last name. The address of a person is also a composite attribute as it can be subdivided into simple attributes such as street, city, country, and state.
Single Valued Attributes
A single-valued attribute is an attribute that can take only a single value for an entity in an entity set. For example, a person’s date of birth is a single-valued attribute as it can only be one date. Examples of single-valued attributes are a student’s roll number, gender, and age.
Multi-valued Attributes
Multi-valued attributes are the attributes of an entity that can have more than one value. For example, an employee’s email ID and mobile number are multi-valued attributes, as there can be more than one email ID and mobile number of the employee(entity).
A double elliptical shape in the ER diagram represents a multi-valued attribute.
Derived Attributes
Derived attributes are those whose value can be derived using other attributes. For example, a person’s age is a derived attribute as its value can be derived by using the “Date of Birth” attribute. A dotted elliptical shape is used to represent a derived attribute in the ERD.
Key Attributes
A key attribute is an attribute that is used to define and identify an entity in an entity set uniquely. It is an essential attribute that makes the entity set either strong or weak. For example, a person’s CNIC number is a key attribute that defines a person uniquely.
Entity Set
An entity is taken as an object having a physical existence, such as a person, house, office, or car, and a conceptual presence, such as a university, job, school, or company. An entity set is the a set of entities.
Attributes describe the properties and are always associated with an entity. They are used to identify an entity uniquely. There are two types of entity sets.
Strong Entity Set
A strong entity set consists of sufficient attributes to define all its entities uniquely. A primary key attribute is always present in a strong entity set. A single rectangle is used for a strong entity set in an ERD.
Weak Entity Set
A weak entity set does not have a key attribute that uniquely identifies the entity; hence this set does not have a sufficient number of attributes. It has a partial attribute, also known as the discriminator, which can identify a group of entities but not the specific one. A double rectangle is used for a weak entity set in an ER diagram.
Figure 3 shows a strong and a weak entity set.
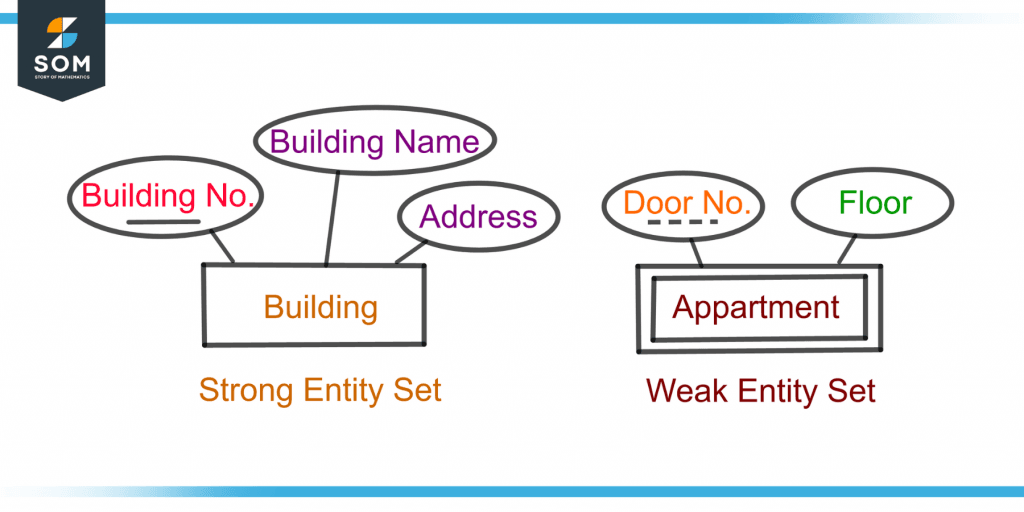
Figure 3 – Demonstration of a Strong Entity Set (Building) and a Weak Entity Set (Apartment)
The “Building” is a strong entity set as it has a key attribute as the building number whereas the “Apartment” is a weak entity set with a partial attribute as the door number.
Types of Attributes in Data Mining
Data mining is finding patterns and extracting valuable information from data sets. The following types of attributes are used in data mining.
Qualitative Attributes
Qualitative attributes are attributes that cannot be measured. They deal with the description and characteristics that are observed subjectively. The following are the types of qualitative attributes.
Nominal Attributes
Nominal attributes have values that include names and symbols. They are also known as categorical attributes as they represent categorical data.
Ordinal Attributes
Ordinal attributes have values with a meaningful order or ranking, e.g., grade and basic pay scale.
Binary Attributes
Binary attributes have only two states e.g. yes or no, true or false. There are two types of binary attributes.
Symmetric Attributes
Symmetric Attributes have both the values of the entity equally important, e.g., gender.
Asymmetric Attributes
Asymmetric attributes have two possible values that are not equally important, e.g., result.
Quantitative Attributes
A quantitative attribute is measurable, hence can be represented as an integer value. There are two types of quantitative attributes.
Discrete Attributes
Discrete attributes have a finite number of values and can also be in categorical form. For example, a profession is a discrete profession with infinite countable values, such as teacher, peon, businessman, etc.
Continuous Attributes
Continuous attributes have an infinite number of values. For example, height and weight are continuous attributes.
Example
Show the graphical representation of different types of attributes of an employee in an ER diagram and explain.
Solution
Figure 4 shows the attributes of an employee(entity).
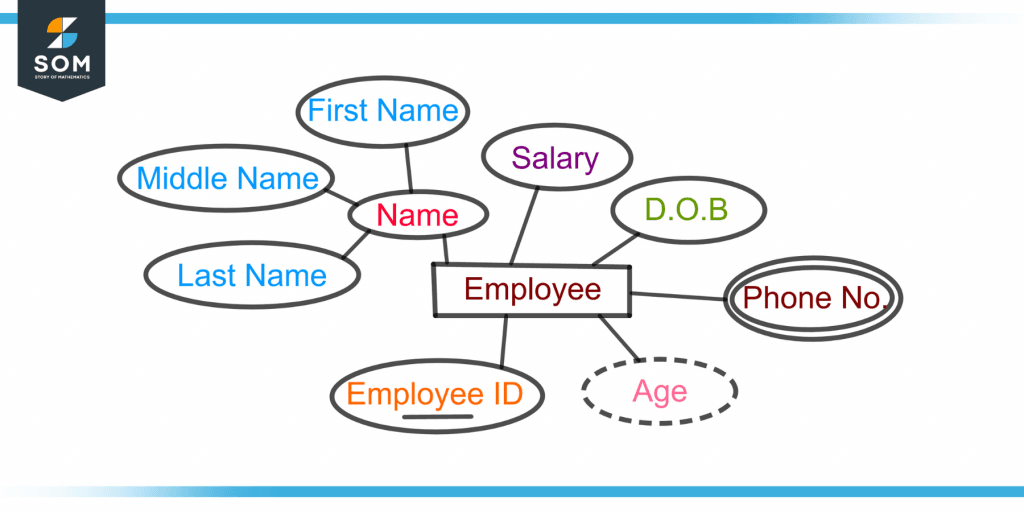
Figure 4 – Graphical Representation of Different Types of Attributes of an Employee
The employee’s name is a composite attribute that is further divided into simple attributes, first name, last name, and middle name. The employee’s age is a derived attribute from the Date of Birth(DOB).
The employee ID number is a key attribute making it a strong entity set. The employee’s phone number is a multi-valued attribute as there can be more than one phone number of the employee.
All the images are created using GeoGebra.
